Dental Implants in Cedar Park, TX
Dental Implants in Cedar Park, TX
At Park Family Dental in Cedar Park, TX, board-certified oral and maxillofacial surgeon Dr. Daniel Ormeni offers complete dental implant care—from surgical placement to final restorations—all in one trusted location. Whether you’re missing a single tooth, multiple teeth, or need All-on-X full-arch replacement, dental implants offer a lasting solution that restores your natural bite, confidence, and quality of life. Using advanced 3D imaging and intraoral scanning, Dr. Ormeni creates personalized treatment plans with exceptional precision and seamless results.
How Dental Implants Restore Your Smile — Function, Strength, and Confidence
Missing teeth impact more than just your appearance—they can affect chewing, speech, bone health, and overall confidence. At Park Family Dental in Cedar Park, Dr. Daniel Ormeni offers complete dental implant solutions that replace both the root and crown of the tooth with a long-lasting, natural-looking restoration.
By placing biocompatible titanium posts directly into the jawbone, implants restore the structure and function of your smile while helping to prevent bone loss. These implants can support everything from a single crown to full-arch dentures—customized for your unique needs.
Quick Facts About Dental Implants:
- 95%+ long-term success rate with proper care
- Can last 20+ years—or even a lifetime
- Helps prevent up to 25% bone loss in the first year after tooth loss
- Restore near-natural bite strength (90–100%)
- Customized for single tooth, multiple, or full mouth restorations
- No damage to adjacent healthy teeth (unlike bridges or partials)
Unlike traditional dentures or bridges, dental implants are the gold standard in tooth replacement—offering unmatched stability, preserving jawbone integrity, and blending seamlessly with your natural teeth so you can eat, speak, and smile with total confidence.
Experience Life-Changing Dental Implant Care in Cedar Park
With Dr. Ormeni’s skilled hands guiding your care, you can expect life-changing improvements in function, comfort, and confidence—restoring not just your smile, but your quality of life.
Specialist Expertise & Precision:
All-in-One Care:
State-of-the-Art Technology:
Sedation Dentistry Options:
Family-Oriented Local Practice:
Durability & Confidence:
Choosing Dr. Ormeni and Park Family Dental means choosing a trusted partner who puts your health, comfort, and lasting results first. Together, we’ll rebuild your smile and confidence with care that truly transforms.
Understanding the Dental Implant Process at Park Family Dental
At Park Family Dental in Cedar Park, Dr. Daniel Ormeni guides you through every step of your dental implant journey with precision and care—combining advanced technology and personalized attention to deliver predictable, natural-looking results.
Comprehensive Consultation
- Your journey begins with a thorough evaluation. Dr. Ormeni uses advanced 3D Cone Beam CT (CBCT) imaging, AI-powered planning, Shining 3D facial scanning, and photogrammetry to assess your bone density, nerve locations, and facial structure. This digital planning allows for precise implant placement tailored to your unique anatomy and treatment goals whether it’s a single tooth, multiple implants, or a full arch restoration.
Implant Placement Surgery
- During a carefully managed procedure, the titanium implant post is surgically positioned in your jawbone. Thanks to state-of-the- art techniques, most patients experience less discomfort than expected and often return to normal activities within 1-2 days.

Healing & Osseointegration
- Over the next 3 to 6 months, your implant will naturally fuse with the surrounding bone in a process called osseointegration, forming a strong and stable foundation for your new tooth or teeth.

Abutment & Restoration
- Once healed, a small connector called an abutment is attached to the implant. Using digital intraoral scanning for maximum comfort and accuracy, Dr. Ormeni then places your custom- designed crown, bridge, or implant-supported denture that looks and functions like natural teeth.

Ongoing Care & Support
- With proper oral hygiene and regular check-ups, your implant restoration will serve you for many years. Our team is here to support your long-term oral health and ensure your new smilestays strong and beautiful.
Schedule your consultation today with oral surgeon Dr. Daniel Ormeni to begin your journey toward a complete, confident smile.
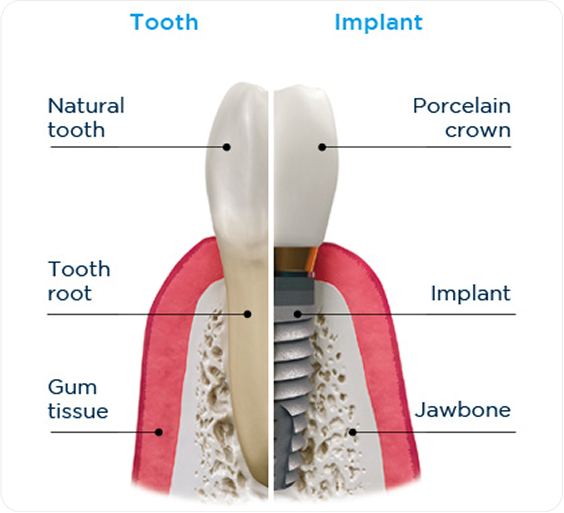

Am I a Candidate for Dental Implants?
Dental implants can benefit most adults with missing teeth, but individual factors influence whether implant surgery and restorations are the right fit for you. At Park Family Dental in Cedar Park, Dr. Daniel Ormeni performs a comprehensive evaluation to tailor the best treatment plan for your unique needs.
Ideal candidates usually have:
Adequate jawbone density to support implants
Healthy gums and good overall oral health
Controlled medical conditions like diabetes
Commitment to maintaining excellent oral hygiene
No active smoking habit (smoking can reduce implant success)
If you have experienced bone loss, don’t worry—advanced solutions such as bone grafting and sinus lifts, or periodontal treatments may prepare your mouth for successful implant placement.
Quick Reference:
- Favorable factors: Non-smoker, good oral care, sufficient bone volume
- Potential concerns: Uncontrolled diabetes, heavy smoking
- Preparation options: Bone grafting, sinus lifts, gum health treatments
During your consultation, Dr. Ormeni will review your health, dental history, and goals, then provide a clear recommendation—whether that’s a single implant, multiple implants, or a full arch restoration.
Cutting-Edge Dental Implant Technology in Cedar Park
Park Family Dental utilizes advanced technology that enhances precision and patient comfort throughout the implant process. Digital treatment planning with 3D imaging allows Dr. Ormeni to visualize your unique oral anatomy and plan ideal implant placement before surgery begins.
Our Cedar Park practice incorporates:
- CBCT scanning for detailed 3D imaging of bone structure
- Computer-guided implant placement for optimal positioning
- Digital impression technology eliminates uncomfortable traditional molds
- CAD/CAM restoration design ensuring perfect fit and natural appearance for single, multiple, and full arch implants
Treatment Aspect
Bone Preservation
Stability
Maintenance
Longevity
Natural Function
Traditional Dentures
No
Limited
Frequent adjustments
5-7 years
30-40%
Dental Implants
Yes
Excellent
Minimal upkeep
15+ years
90%+
What to Expect After Your Dental Implant Surgery & Restoration
We’re committed to supporting your comfort and healing every step of the way. Most Cedar Park patients experience minimal disruption to their daily routine following dental implant surgery and restoration.
Initial Recovery (First 24–48 Hours):
- Mild discomfort managed easily with prescribed pain relievers
- Minimal swelling reduced with ice packs
- A soft food diet is recommended to protect healing tissues
First Week to Two Weeks:
- Gradual return to your normal diet as comfort allows
- Gentle brushing around surgical areas to maintain hygiene
- Avoid strenuous activities to promote healing
Healing & Integration:
- Osseointegration (the implant fusing with your jawbone) typically takes 3 to 6 months
- Follow-up appointments with Dr. Ormeni ensure your healing is progressing smoothly
Long-Term Success:
- Maintain routine dental check-ups and professional cleanings every six months
- Consistent at-home care is essential to protect your implant-supported crown, bridge, or denture

Most patients return to normal activities within 1 to 3 days, enjoying renewed function and confidence as their smile heals. Throughout your recovery, Dr. Ormeni and our Cedar Park team remain available to answer questions and provide personalized aftercare guidance to ensure your journey is as smooth and successful as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dental Implant Surgery
How painful is dental implant surgery?
Most patients report minimal discomfort during recovery, comparing it to a tooth extraction. Dr. Ormeni employs advanced techniques to ensure comfort throughout the procedure. Unlike other dental offices, we also have every option available for sedation dentistry including IV sedation and can discuss which would be right for you.
How long do dental implants last?
With proper care, dental implants can last 20+ years, with many lasting a lifetime. Success rates for dental implants generally exceed 95%, making them one of the most reliable tooth replacement options available.
How do I care for dental implants?
Maintain regular oral hygiene practices including brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings—just like natural teeth.
Can implants be placed immediately after extraction?
In select cases, Dr. Ormeni may place implants immediately after tooth extractions, depending on bone quality and overall site condition. During your consultation, he will determine if this approach is suitable for your situation.
How long is the entire process from start to finish?
Typically 3-6 months from initial surgery to final restoration, depending on healing time and specific treatment needs—whether you are receiving single tooth, multiple, or full arch implants.

